Medical malpractice cases hang by the thread of evidence that thrives in medical records. Attorneys rely on accurate, well-organized medical record analysis to determine whether malpractice occurred and to evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of a claim. Understanding common legal terms in medical malpractice cases is essential at this stage.
To establish medical negligence, four core elements need to be proven: duty of care, breach of duty, causation and damages. For attorneys, claimants and medical reviewers alike, a clear understanding of legal terminology is crucial—especially with cases getting more complex and data-oriented in today’s medico-legal environment.
Take a look into an updated, easy-to-read overview of common legal terms used in medical malpractice cases. Many of these terms also apply to personal injury litigation more broadly.
Alternative Dispute Resolution
- Arbitration: A method of resolving disputes outside the courtroom, frequently used in medical malpractice litigation to avoid prolonged trials. An independent arbitrator hears arguments from both parties and issues a binding or non-binding decision, depending on the agreement.
Legal Documents and Court Filings
- Affidavit: A voluntary written statement of facts confirmed under oath, often used to support motions or claims in medical negligence cases.
- Pleadings: Formal written statements filed by the parties outlining the facts and legal grounds of their case, including complaints, answers, and motions.
- Subpoena: A court-issued order requiring an individual to appear for testimony and/or produce documents or evidence.
Damages and Compensation
- Damages: Monetary compensation awarded to an injured party.
- General damages: Pain, suffering, and loss of quality of life
- Special damages: Medical expenses, lost wages, and other financial losses
- Compensatory Damages: Designed to reimburse the claimant for actual losses such as medical bills, lost income, and emotional distress.
- Punitive Damages: Awarded to punish particularly reckless or intentional misconduct and to deter similar behavior in the future.
Evidence and Discovery Process
- Discovery: A pre-trial process allows both sides to exchange relevant information, documents, and evidence related to the case.
- Deposition: Sworn, out-of-court testimony taken during discovery, typically involving attorneys questioning witnesses.
- Interrogatories: Written questions submitted by one party and answered in writing under oath by the opposing party.
- Exhibit: A document or physical object presented as evidence during a trial or hearing.
- Evidence: Includes testimony, documents, records, physical objects, and other materials presented to support or refute claims.
Court Decisions and Case Outcomes
- Directed Verdict: A ruling made by a judge when the evidence overwhelmingly favors one side, without sending the matter to a jury.
- Judgment: The court’s final decision in a case. This may include summary judgment, default judgment, or judgment notwithstanding the verdict.
- Dismissal with Prejudice: A case dismissal that permanently bars the plaintiff from filing another lawsuit on the same claim.
- Dismissal without Prejudice: A dismissal that allows the plaintiff to refile the case in the future.
Standards of Care and Professional Conduct
- Established Customary Standard of Care: The level of care and skill that a reasonably competent healthcare professional would provide under similar circumstances.
- Disciplinary Hearing: A professional review conducted by a regulatory or licensing authority to evaluate alleged misconduct.
- Liability Risk: The potential exposure to legal responsibility arising from negligent or wrongful acts.
- Indemnity: An agreement in which one party agrees to financially protect another against specific losses or claims.
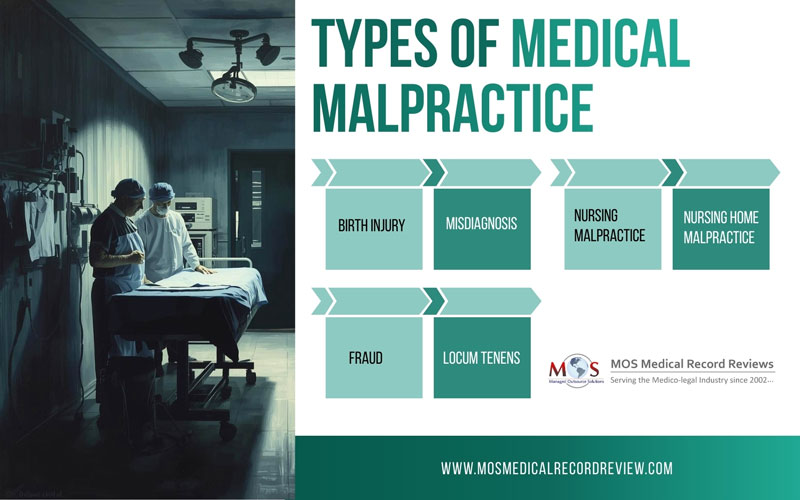
Types of Medical Malpractice
- Birth Injury: Physical harm suffered by an infant during labor or delivery, potentially resulting in long-term disability or death.
- Misdiagnosis: An incorrect or delayed diagnosis caused by failure to meet the accepted standard of care.
- Nursing Malpractice: Negligent or intentional acts by nursing professionals that result in patient harm.
- Nursing Home Malpractice: Injuries caused by neglect or intentional misconduct within long-term care facilities.
- Fraud: Intentional deception by a healthcare provider, including concealment of malpractice or misrepresentation that adversely affects patient care.
- Locum Tenens: This is a term for physicians who practice on a temporary or substitute basis within healthcare facilities.
Trial Strategy and Witnesses
- Rebuttal: Evidence introduced to counter or refute claims made by the opposing party.
- Rebuttal Witnesses: Witnesses who are presented specifically to dispute or weaken evidence offered by the adverse party.
Why Accurate Medical Records Matter More Than Ever
Medical malpractice cases today often involve large volumes of fragmented, multi-source medical records, including EHRs, diagnostic reports, and specialist notes. Without proper organization and analysis, critical details can be overlooked—impacting case strategy, settlement decisions, or trial outcomes.
Professional medical record review services help attorneys identify relevant records, establish timelines, and produce concise case summaries that support informed legal decision-making. In an era of increasingly complex healthcare data, clarity and accuracy are no longer optional—they are decisive.
Complex Medical Records Shouldn’t be a Problem
Strengthen your malpractice case strategy with accurate & litigation-ready medical summaries